Ball Bearing - Angular Contact Bearings
About Angular Bearings
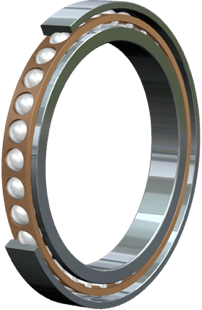
Angular contact bearings are comprised of an inner ring, an outer ring, a ball and a cage, with either one or two raceways built onto the internal or external rings. A prominent 15°- 40° contact angle forms in relation to the bearing axis, which allows for the displacement of the bearing.
An augmentation of the bearing contact angle increases the carrying capacity. Similarly, as the axial load is maximized, the radial load diminishes, accommodating to combined loads where the radial and axial loads work in unison. The load is transferred between the raceways, and the asymmetry allows for the mechanism's high thrust capacity.
Engineering & Design
Angular contact bearings are designed to suit various usages, and are available in a wide array of accuracies and tolerances, measured by the standardized ABEC bearing rate scale.
These bearings can be produced from numerous materials to provide stainless steel, plastic, and ceramic angular contact bearings. The cage assemblies are usually available in polyamide, steel, or brass. In order to enhance the device's performance and provide corrosion resistance, special cage materials, lubricants, preloads and coatings may be added. Additionally, many models offer an external chrome or cadmium plating protective shield.
These bearings are available in various dimensions. Standardized sizes categorize these bearings according to the outer diameter (including the bearing housing but excluding the attached flange), the bore size, and the external ring's width.
Models
There are three primary types of angular contact ball bearings:
Single-Row Angular Contact Ball Bearings: These are characterized by their potential rigidness and high-accuracy. They are capable of holding significant high-thrust axial and radial loads, but the contact angle allows for the loads to function in only one direction. The radial load triggers an axial force component, which requires either two or more opposing bearings to be used simultaneously. The thoroughly designed contact angle on the raceway and shoulders allows the high axial loads to run smoothly.
Double-Row Angular Contact Ball Bearing: These are used as fixed-end bearings and are constructed by intertwining both the inner and outer rings of two single-angular contact bearing into one bearing device. This allows the axial loads to operate in both directions, and offers a compact, rigid operating capacity.
Four-Point Contact Ball Bearings: These bearings, with 35° angles, are optimal for heavy axial loads. The inner ring is split in two, allowing the bearing to hold a significant axial load in a single direction.
A primary differentiating factor between different angular contact bearings is the presence (and type) of seals and shields. These add-ons provide extra protection against external pollutants and retain the mechanism's lubrication. While seals provide a more lucrative lubrication, shields are less likely to affect the bearing's speed capacity.
Applications
Angular contact bearings are typically selected for their high-speed, high-precision antifriction capacities. Examples include, but are not limited to: the agriculture industry, the chemical industry, the general industry, and utilities manufacturing.
Haven't found what you want? Look here