Types of CV Joints and their design
CV Joints also known as Constant Velocity Joints are used in automobile because of their ability to transmit power at a variable angle in a drive shaft. This apparatus can transmit power at a constant rotational speed and because of their property of transmitting power at a constant speed, they are also known as Homo kinetic joints. Additionally CV Joints do not put excessive pressure or create excessive amount of friction while operating that make them one of the most suitable solution for using in automobiles.
Usually these joints are used in front wheel drive cars and vehicles while some modern vehicles with independent rear suspension and rear wheel drive also use these joints in shafts. Usually these joints are protected by rubber boot that keep the apparatus safe from containments which can reduce the overall performance and life of these joints. There are several different types of CV Joints that vary in design, structure, applications, and CV joints prices.
How CV Joints work?
CV Joints are used in both ends of the drive shafts. Inner joint connects the drive shaft to the transmission while the outer joint connects wheels with the drive shaft. Although this design and method is usually applied to front wheel drive vehicles because of the moving front wheels but in some rear wheel drive vehicles and trucks they are used too. The purpose of using CV Joints is to transfer the torque at a constant speed from transmission to the wheel with minimum friction and loss.
Not only that but these ball bearing joints also bear up and down movements caused by suspension. In front wheel drive vehicles, these joints transfer the torque as it is to wheel from transmission during turns. In those vehicles, two types of joints are used to accommodate different movements and carrying angles. Ball type joints are used as outer joints to connect shafts to the wheels while tripod type joints are used to connect transmission with the drive shaft.
Common CV Joint Problems
Although these joints are built with accuracy but because of their use and harsh working environment, CV joint problems might occur that ultimately lead to reduced efficiency or performance. Most of the CV joints can last very long and they can work perfectly for many years but CV joint problems all depend on the rubber or plastic boot that protects them. These ball bearing joints are packed with special lubrication that is important for performance and durability. That lubrication and whole joint is usually sealed tight with plastic or rubber boot.
Usually these ball bearing joints do not need any kind of repair or maintenance as long as the plastic seal or rubber is not damaged. It is not uncommon to see a vehicle with thousands of miles and still with original joints. But CV joint problems occur when that plastic or rubber boot gets damage or cracks. These CV joint problems might be caused because of several different reasons. Once the rubber or plastic that protects the whole apparatus and lubrication cracks, the lubrication comes out and containments like dirt and water gets in.
Those containments damage inner parts of these ball bearing joints that eventually cause CV joint problems that reduce overall performance, efficiency and life of the apparatus. As you can imagine the inner joints work significantly lesser than the outer joints. So, ultimately outer joints get damaged first as compared to their counterparts. You can identify some common CV joint problems easily by analyzing the situation. If the joints are creating a clicking noise when turning then it is highly likely the CV joint problems are due to the outer joints being damaged.
If the joints create clunking sound only when accelerating or decelerating then the inner joints are damaged in a front wheel drive vehicles. On the other hand, this sound could be caused by damaged inner or outer joints in rear wheel drive vehicles with independent rear suspension. If you hear a humming noise or a constant noise that is not clicking then it is because of lack of lubrication. As CV joints come with sealed lubrication, it is highly likely the constant velocity joint problems are caused by the plastic or rubber boot that protects the lubrication being damaged.
If you experience a vibration during acceleration then it is because of inner or outer CV joint problems. Although the reasons behind this kind of vibrations could be different in front wheel drive, rear wheel drive and all wheel drive vehicles so you have to diagnose the issue more thoroughly. Additionally, if the vibrations increase with speed then it is because of the out of order CV joint that is not reliable anymore. Because the CV joint problems create imbalance between wheel and shaft or between shaft and transmission, the whole system starts vibrating at higher speed.
Fixed and Plunge Joints
The difference between fixed and plunge joints is quite easy to understand and obvious. These joints are either fixed that means they cannot move in and out to change the overall length or they can be plunge joints that means they can do in and out movement to compensate with the length. The applications of fixed and plunge joints are different because of their design limitations and structure.
In a front wheel drive vehicle, the inner or inboard joint is a plunge joint while the outer joint or outboard joint is a fixed joint because it has to work on a varying angle because of steering and suspension movement. Because of the half shaft used in front wheel drive cars and vehicles, only one joint on each end has to be a plunge joint. On the other hand, in rear wheel drive cars and vehicles with independent rear suspension, on joint on each end of the shaft has to be fixed and the other one has to be plunge joint.
Or both can be plunge joints because the wheels are not used for steering and the operating angle is not as great as in case of front wheel drive vehicles. Because of lesser operating angle needed, one or both joints at each end of shaft could be plunge joints.
Types of CV Joints
There are several different types of CV joints and they are categorized by their position, function and design, all of which you can find for the lowest CV Joint prices with our bearing finder. Usually these ball bearing joints are called inboard and outboard joints in automobiles. In front wheel drive vehicles, the inner joints that connect shaft with the transmission are called inboard joints while the outer joints that connect shaft with the wheel are called outboard joints. On the other hand, in rear wheel drive vehicles with independent read suspension, the joints which are positioned near the differential are called inboard joints while the joints which are closer to wheels are called outboard joints.
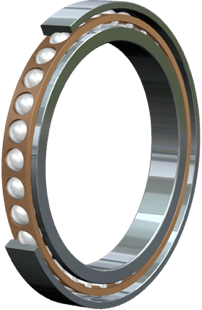
Fixed Ball Type Joints
Ball type CV Joint is a common type of CV Joints that is distinguished based on its design. A ball type joint could be a fixed joint or a plunge joint depending on the requirements and applications. Fixed ball type joints are also known as Rzeppa joints and they are known for their performance, frictionless motion and durability. There are four basic components of a Rzeppa joint which are inner ball race, balls, a cage that holds those balls at the right position and the outer housing.
Usually six balls are used in this kind of ball bearing joint, and they not only servers as ball bearings between inner and outer rings but they also move in different directions and angles to transmit torque at different varying angles. The movement of balls does not depend on the operating angle but they always bisect the shaft angle. Because of this particular movement, the apparatus doesn�t vibrate even at higher speed. Obviously the input speed and the output speed of the ball bearing joint remain equal and that�s why it is given the name of Constant Velocity Joints.
The role of cage is very important in the whole process because it helps balls align at right angle and position. If the cage deforms because of any possible reason, the performance of ball bearing joints reduces dramatically and they usually create a clicking sound. Another variant of ball type joints is called dish type joint that is usually used in Volkswagen and in some modern rear wheel drives vehicles, although the basic design and structure of dish type joint is almost identical to the Rzeppa joint.
Plunge Ball Type Joints
Plunge ball type joints usually come in two types which are double offset joint and cross groove joint. Both of these types have different operating angles and plunge depth. Plunge ball type joints have compact design and angles grooves. Double offset joints offer a relatively higher operating angle that could be up to 25 degrees as well as a relatively deeper depth that could be up to 2.4 inches. This type of joints is usually used in half hafts of font wheel drive cars and vehicles as well as in some all wheel drive vehicles.
The other type of plunge ball type joints is cross groove joints which come with a relatively lower operating angle that could be up to 22 degrees. As compared to their counterpart, these joints also have a lesser plunge depth that could be up to 1.8 inches, although because of the same plunging motion of inner and outer races lesser depth is required. Cross groove joints are usually used in front wheel drive vehicles as inboard joints as well as in shafts of rear wheel drive vehicles with independent rear suspension.
Fixed Tripod Joint and its design
Tripod joints have some design limitations and because of those particular properties, these joints are used in limited front wheel drive vehicles. Fixed tripod joints come with a significantly higher operating angle but they are not suitable for most of the automobile application because they cannot be removed from the shaft. In case a fixed tripod joint goes bad or cracks, the whole shaft and ball bearing joint would be replaced.
In some front wheel drive vehicles these joints are used as outboard joints because of their higher operating angles. The design of fixed tripod joints is quite simple as both the input and output shafts are mounted with the help of three roller bearings and a steel cage is required to hold the joint.
Plunging Tripod Joint and its design
This type of tripod joints are usually used in some front wheel drive vehicles as inboard plunge joints. These joints consist of a central tripod that is usually known as spider because of its design. Because of the flower like shape of apparatus fitted with spherical rollers, it is called tulip. There are two variants of outer housing used in this kind of ball bearing joints and both of these types have different applications as well as structure.
In some cases, the outer housing of these ball bearing joints is closed that means the roller and races are enclosed in the apparatus. On the other hand, in some joints the outer housing open with a flower like shape.